The term 'Asia Pacific' become popular in the late 1980's in commerce, finance, and politics. It comprises the broader regions of Asia and Oceania. Within these two regions it can be further broken down as follows:
Asia
East Asia
Southeast Asia
North Asia (Siberia)
South Asia
Oceania
Australasia
Melanesia
Micronesia
Polynesia
Asia
Oceania
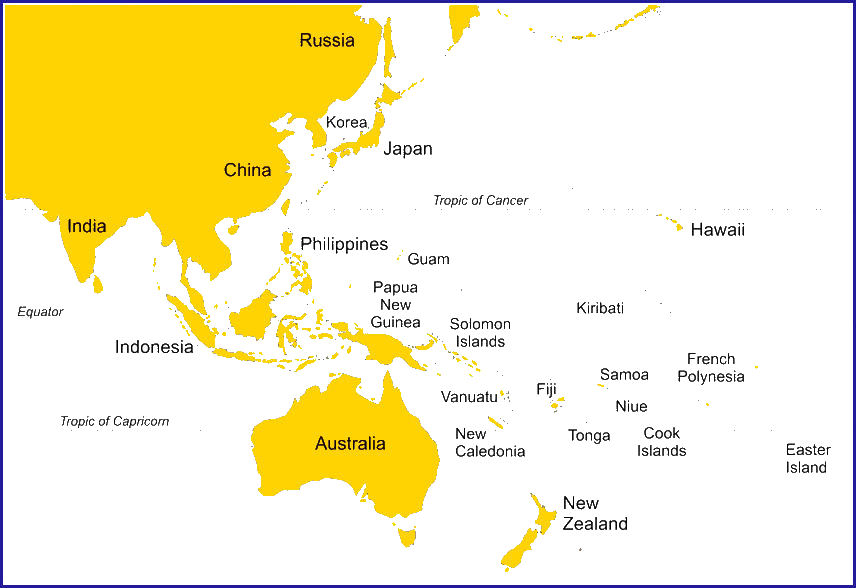
Map of the Asia Pacific region showing the major countries/territories
East Asia
South East Asia
Far East Asia (Siberia)
South Asia
Australasia
Melanesia
Micronesia
Polynesia
The population of Asia Pacific is in excess of 4.7 billion which represents approximately 60 % of the world population, due largely to the two largest countries in the world, China and India, being part of the region.
A significant free trade agreement was implemented between 15 of the Asia Pacific nations in November 2020. The world's biggest trade deal in terms of GDP, the member nations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam believe it will drive economic growth in the region. Referred to as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), the agreement was signed on Sunday 14 November 2020. The pact lowers tariffs, opens up the service sector and sets common trade rules within the bloc. The agreement covers trade, services, investment, e-commerce, telecommunications and copyright. The China-backed agreement is seen as a replacement and expanded version of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), a now-defunct trade initiative.

